Making Sense of Total Addressable Market or TAM
Key Takeaways
TAM's Crucial Role: Total Addressable Market (TAM) is essential for understanding market potential and guiding investment and business strategies.
TAM's Dynamic Nature: As businesses grow, their TAM can expand through product innovation, market entry, and strategic shifts.
Impact on Strategic Decisions: A clear grasp of TAM helps companies allocate resources wisely, prioritize markets, and adapt products to effectively meet market demands.
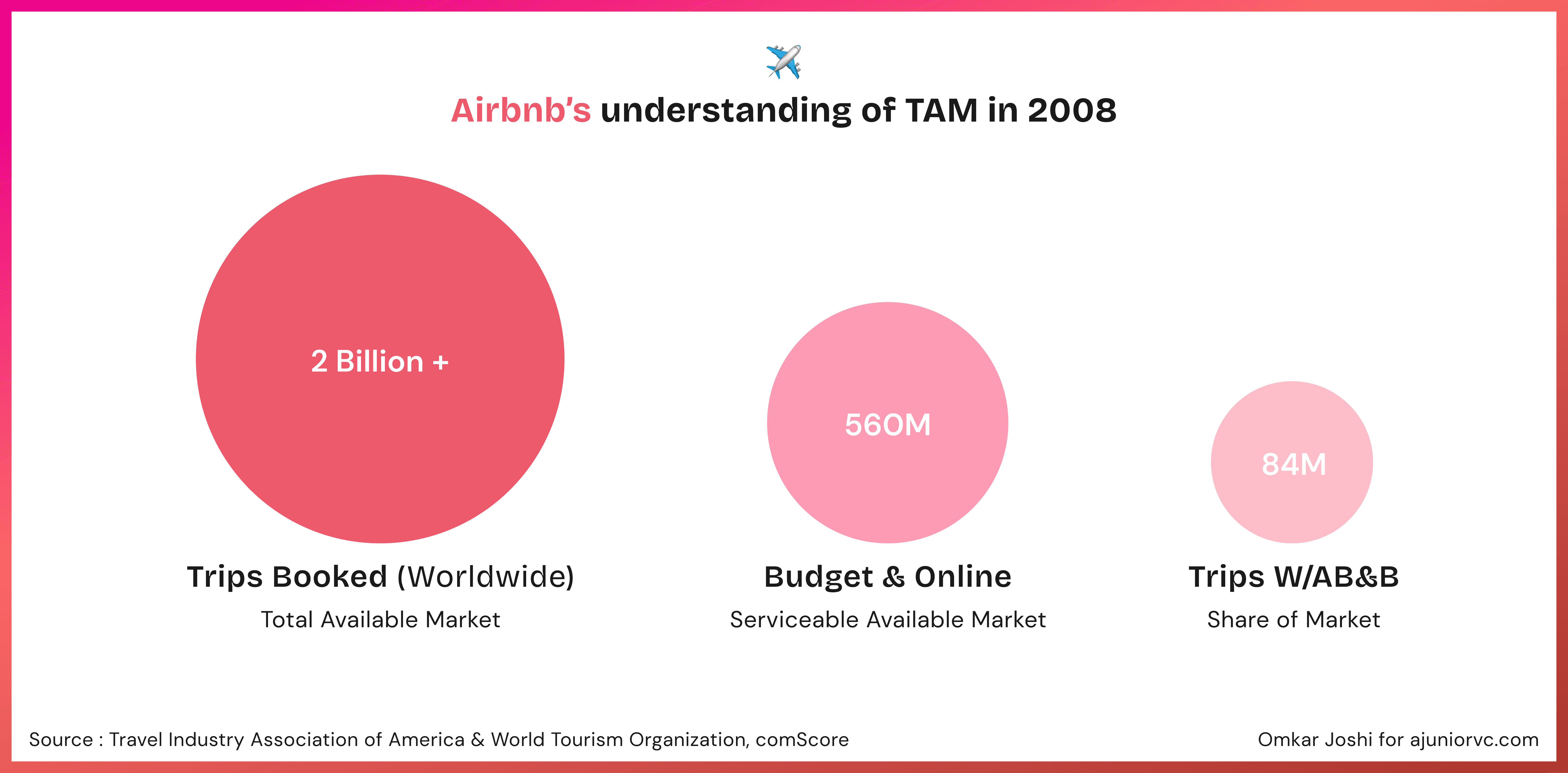
Globally 2 Billion+ trips booked: Airbnb pitched to its investors in 2008. What does this mean?
Let’s understand this further.
When Airbnb pitched its business to investors in 2008, it proposed tapping into a global travel market with over 2 billion trips booked annually.
This broad market perspective outlined its Total Addressable Market (TAM), indicating the overall revenue opportunity available or the complete market demand for its service, assuming it captured a certain percentage of this market.
Fast-forward to 2024. Airbnb reports approximately 450 million bookings per year, and this figure is growing at around ~10% year over year.
So does this mean Airbnb captured 25% of its original TAM in these 16 years?
It's not a straightforward assessment.
Initially, renting a bed and breakfast was novel, but as this idea became mainstream and travel increased, the category expanded. Airbnb's initial TAM also grew, adjusting to market conditions and consumer behaviour changes.
Understanding TAM is crucial for businesses and investors as it delineates a company's potential market size and revenue generation potential.
The core idea is that a company can't outgrow its TAM but can capture a certain fraction of it as market share.
For instance, Airbnb's clear articulation and understanding of its TAM have allowed it to strategically explore and dominate the lodging and travel sector. As the travel and temporary lodging market continues to evolve, so does the TAM, providing a new target for Airbnb's ongoing business strategies.
This nature of TAM underscores the need for continuous market analysis and adaptation of business strategies to align with evolving market conditions, maximising potential reach and profitability within the addressable market. Such insights help in strategic planning and play a crucial role during investment evaluations, as they provide a ceiling on the possible growth and scale that businesses can aim for.
The Role of TAM in Pitch Decks
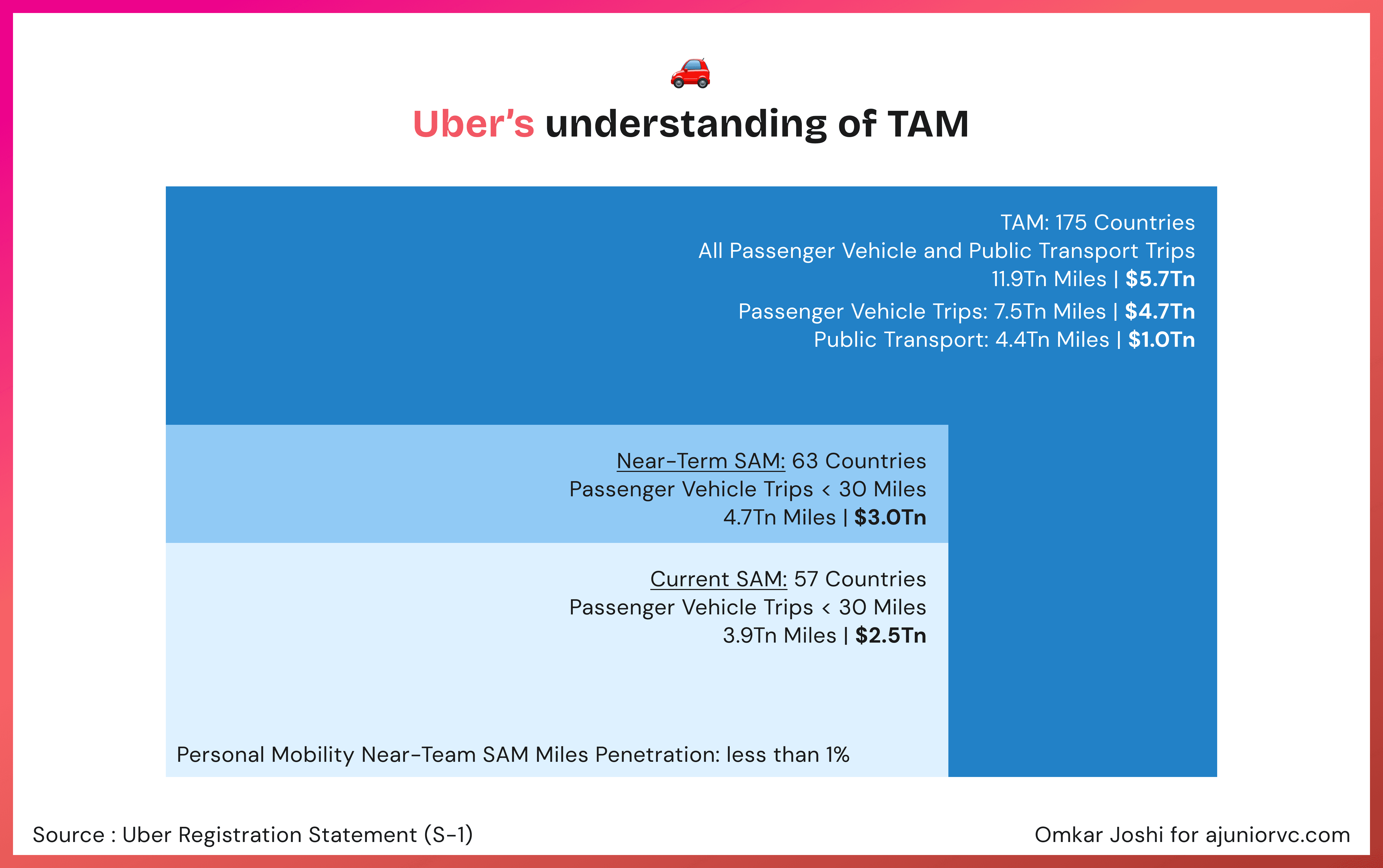
Let's take the example of Uber, a company that most of us have not only heard of but likely also used. When Uber initially pitched and then filed for its IPO (see Figure 1), it provided a comprehensive and detailed definition of its market opportunity. It serves as an excellent case study to understand how strategic market assessment can shape both founder and investor perspectives.
Company’s perspective
From a company’s perspective, strategically thinking about the Total Addressable Market (TAM) involves more than just understanding the market's vastness—it's about identifying where to allocate resources effectively and how to scale operations to capture significant market share over time.
For Uber, this would have entailed a multi-faceted approach:
Strategic Resource Allocation
Market Prioritization: Deciding which markets to enter first is crucial. This decision would be based on various factors including market size, regulatory environment, and existing competition. For Uber, focusing on urban areas with high population density and a greater reliance on public transport could provide quicker traction and better margins.
Product Adaptation: Uber might also consider how different market segments have different needs and adapt their service offerings accordingly. For example, in markets where short trips are more common, focusing on UberX or UberPOOL could be more profitable, whereas in cities with a higher demand for premium services, pushing UberBLACK or UberSUV could be more strategic.
Technology Investment: Allocating resources toward technological advancements is key. Enhancements in the app's interface, route optimization algorithms, and safety features could help Uber increase its market share by improving customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Scaling to Capture TAM
Phased Expansion: Understanding that capturing the TAM is a long-term and ongoing process, Uber's strategy likely involves phased expansion. Initially, establishing a strong presence in key markets before scaling out to more regions gradually helps mitigate risks and manage resources more efficiently.
Partnerships and Collaboration: Forming strategic alliances could be crucial for rapid expansion. Collaborations with local businesses, governments, and transport agencies can help Uber integrate more deeply into the fabric of local transportation networks.
Customer Acquisition and Retention: Investing in marketing and customer relationship management helps acquire and retain new users. Promotions, discounts, loyalty programs, and responsive customer service are tactics that help build a strong user base.
Regulatory Navigation: Navigating the complex landscape of local and international transport laws is essential. Hiring experts in public policy and engaging with stakeholders early can facilitate smoother expansions and operations in new markets.
Founder's Vision and Execution
The founders would need to balance aggressive growth and sustainable business practices. This includes:
Financial Management: Ensuring the expansion cost does not exceed the potential returns. This involves careful financial planning and possibly securing additional funding rounds based on market penetration milestones.
Cultural Adaptation: It is crucial to adapt the business model to fit the cultural and operational nuances of new markets. This may include localizing the service offering and marketing strategies to resonate with local consumers.
Investor’s perspective
Investors, especially those in venture capital, utilize the Total Addressable Market (TAM) as a critical gauge to evaluate an investment opportunity's potential scale and profitability. Here’s a detailed breakdown of how investors perceive and utilize TAM:
Assessing the Market Size and Scope
Understanding TAM: Investors would scrutinize Uber's Total Addressable Market data, which indicated extensive global opportunities across various transportation sectors.
Scope for Expansion: The vast TAM would suggest potential for scaling into new regions and services, crucial for long-term growth prospects.
Evaluating Scalability and Market Penetration
Scalability: Investors would assess Uber’s ability to scale based on its technology, operational efficiency, and network effects within the transportation sector.
Market Penetration Strategies: Understanding how deeply Uber could penetrate segmented markets (e.g., short commutes, food delivery) would be critical to validating the practical capture of the stated TAM.
Revenue Projections and Growth Strategy
Revenue Potential: From the TAM, investors would derive potential revenue benchmarks, estimating how Uber’s market capture strategies align with revenue growth targets.
Growth Strategy Evaluation: Analyzing Uber’s growth strategies—such as geographic expansion, product diversification, and technology innovation—would help investors predict how these strategies might accelerate the company’s market share capture within the TAM.
Risk and Regulatory Considerations
Market and Regulatory Risks: Investors would consider potential regulatory challenges and market risks that could impact Uber’s ability to exploit the full TAM.
Competitive Landscape: Understanding competitive threats within the TAM would help investors assess whether Uber’s business model could sustain pressures and maintain its competitive edge.
Exit Valuation and ROI Estimations
Potential Exit Scenarios: Based on the size of TAM and Uber's market position, investors would project various exit scenarios, including public offerings or acquisitions.
ROI Calculation: Estimating the return on investment by considering Uber’s potential to grow within the TAM and achieve high exit valuations. For example, capturing 10% of a $100 billion TAM would significantly impact the ROI for early investors.
Long-term Value Creation
Sustainability of Growth: Beyond immediate financial returns, investors would evaluate how Uber's positioning within the TAM could contribute to sustained growth and long-term value creation.
Impact of Innovations: Consideration of how Uber’s continuous innovations might expand the TAM itself or improve penetration efficiency, thus creating new value streams.
Sample Investment and Returns Analysis
Initial Investment
Fund Size: The fund has a total capital of $1 billion.
Investment Amount: Assume a venture capital (VC) fund invested $50 million in Uber [5% allocation of the total fund size].
Fund Return Expectations
Return Objective: The fund aims to achieve returns that can cover the entire fund amount, targeting investments that could individually return at least $1 billion.
Uber’s Market Opportunity and TAM
TAM Analysis: Despite Uber’s projections of a TAM in the trillions, the fund conservatively estimates Uber's TAM at $100 billion globally, considering only the market segments Uber is most likely to capture.
Market Penetration Goals: The fund estimates that Uber targets capturing about 1% of this TAM, translating into a realistic revenue goal of $1 billion.
Exit Valuation and Revenue Targets
Revenue Target at Exit: To meet investment return targets, Uber needs to reach $1 billion in annual revenue by the fund's exit.
Exit Valuation Multiple: Assuming a conservative exit revenue multiple of 10x, the expected company valuation at exit would be $10 billion.
Stake and Valuation: With the fund holding a 10% stake in Uber, the targeted share of the exit valuation would be $1 billion. Also, if the fund does not participate in subsequent funding rounds, its initial 10% stake in Uber could be diluted to a lower percentage, reducing its share of the exit valuation proportionally (e.g., from 10% to 7% leading to a decrease in potential exit proceeds from $1 billion to $700 million).
Growth Potential for Next Buyer
Post-Exit Growth Expectation: After the fund's exit, the next buyer or public market investors during an IPO would expect Uber to continue growing. A projected 50% growth over the next 5 years would increase Uber’s revenue to $1.5 billion, supporting a continued high valuation.
ROI Calculation
Return on Investment: If the VC’s $50 million investment secures a 10% equity stake at the time of IPO, and Uber reaches a $10 billion valuation at exit, the VC’s return would be 20x. This translates to a $1 billion return on their initial $50 million investment.
TAM Expansion
In earlier sections, we discussed defining the Total Addressable Market (TAM) and discussed how crucial it is for startups and established companies to understand the potential market size they're entering.
But here's the thing—TAM isn't always a static figure.
As companies evolve, often so does their TAM. It's a dynamic number that shifts as businesses leverage their existing distribution networks, explore new verticals, and venture into allied services.
Take Zomato, for instance. It's a fascinating story of how a company can significantly expand its TAM by diversifying its offerings and tapping into new markets.
Starting Out: Foundation and Initial Expansion
Original Service: Zomato began as a restaurant discovery platform, initially capturing the TAM of diners looking to explore dining options.
Expansion into Table Reservations: By adding table reservation capabilities, Zomato enhanced user engagement and tapped into a larger TAM by attracting users who prefer planned dining experiences and might not frequent the platform solely for reviews.
Impact: This service expansion directly increased the frequency of customer interactions with the platform, broadening Zomato's TAM to encompass a more extensive customer base that values convenience and discovery.
Strategic Move into Food Delivery
Rationale: Observing a surge in demand for home food delivery, Zomato decided to leverage its existing restaurant network to offer delivery services.
Impact: This pivot expanded Zomato's TAM from those interested in dining out to virtually anyone interested in restaurant food, significantly broadening its market to include a larger segment of customers preferring home dining. The delivery service also increased the platform’s transaction volume, contributing to revenue diversification and growth.
Geographic Expansion: International Scaling
Strategy: Zomato targeted international markets with dining cultures similar to India's, such as the UAE and Southeast Asia.
Impact: Each new market brought distinct consumer behaviors and dining preferences, increasing Zomato’s global TAM. This strategy diversified Zomato's revenue streams and mitigated risks associated with dependency on the Indian market alone.
Hyperpure: Tapping into B2B
Introduction of Hyperpure: Recognizing the need for reliable ingredient sourcing among restaurants, Zomato launched Hyperpure.
Impact: By entering the B2B space, Zomato expanded its TAM to include restaurant businesses, not just end consumers. Hyperpure addressed a critical supply chain gap, strengthening Zomato’s relationships with its restaurant partners and enhancing the quality of offerings delivered to end-users.
Zomato Pro: Membership Program
Initiation of Zomato Pro: To combat increasing competition and improve customer retention, Zomato introduced a loyalty program offering benefits like discounts and exclusive deals.
Impact: Zomato Pro helped solidify user loyalty and increase transaction frequency, expanding Zomato’s TAM by appealing to a segment of users who value premium service and are likely to engage more frequently.
Acquisition of Blinkit
Rationale: Recognizing the growing demand for instant delivery services, Zomato acquired Blinkit, a leader in the quick-commerce space known as Grofers.
Impact: This acquisition allows Zomato to tap into the rapidly expanding quick-commerce market, considerably enlarging its TAM. It broadens Zomato's offerings beyond food delivery to include groceries and essentials, reaching a wider audience that values speed and convenience.
Zomato Legends
Rationale: With 'Zomato Legends,' Zomato aims to celebrate and spotlight iconic restaurants known for their unique and traditional dishes. This initiative caters to culinary enthusiasts who seek authentic and culturally significant dining experiences.
Impact: By highlighting legendary eateries, Zomato enriches its content and attracts a niche market of food lovers interested in premium and heritage dining experiences. This helps expand its TAM to include customers seeking exclusive culinary adventures, enhancing user engagement and loyalty.
Despite the apparent success and positive reception, Zomato decided to discontinue the "Zomato Legends" program. This decision may have been driven by several factors:
Strategic Refocus: Zomato might be shifting its strategic focus towards scaling newer, potentially more profitable avenues like Zomato Pro or hyperpure, aligning resources with broader business goals that promise higher returns or are more sustainable in the long run.
Operational Challenges: Managing such a program can be operationally intensive, requiring dedicated resources for curating and maintaining up-to-date, accurate information about each legendary eatery. The logistics involved in ensuring that these restaurants meet a consistent standard or dealing with fluctuations in quality could have become cumbersome.
Market Dynamics: Changes in consumer behavior, such as increased demand for quick service restaurants (QSRs) or food delivery due to lifestyle changes, might have diminished the interest in traditional dine-out experiences. The COVID-19 pandemic has also altered dining habits, potentially impacting the relevance of a program focused on dine-in experiences.
Financial Considerations: The cost-effectiveness of the program might have come under scrutiny. If the revenue or brand enhancement from "Zomato Legends" did not justify the operational expenses, discontinuation might be seen as a move to optimize profitability.
Multi-Restaurant Cart Feature
Rationale: In response to customer feedback for more versatile ordering options, Zomato introduced the ability to combine orders from multiple restaurants into a single cart.
Impact: This feature addresses a common customer pain point by allowing varied dining preferences within a single order. It significantly enhances customer satisfaction and convenience, encouraging larger orders and more frequent use of the platform. Thus, it expands its TAM to groups and event planners who often need to cater to diverse tastes.
Events and Movie Ticketing
Rationale: Expanding into events and movie ticketing through a partnership with Paytm allows Zomato to tap into another aspect of urban entertainment and leisure spending.
Impact: By offering a more integrated lifestyle platform that includes dining, events, and entertainment, Zomato significantly broadens its customer base to include not just foodies but also general urban leisure seekers. This diversification helps increase user stickiness and opens up new revenue streams by cross-selling services.
And That’s a Wrap
Understanding your Total Addressable Market (TAM) is crucial for impressing investors and making smart, strategic decisions. It’s about knowing where you can really shine and how big the playground is.
But remember, the market doesn’t stand still—neither should your strategy. Keep your data fresh, stay alert to new trends, and be ready to shift gears when needed.
Next time, we’ll dive into some common traps with TAM calculations and how to sidestep them. Expect practical tips that’ll keep you on top of your game. Stay tuned, and let’s keep making smart moves together!